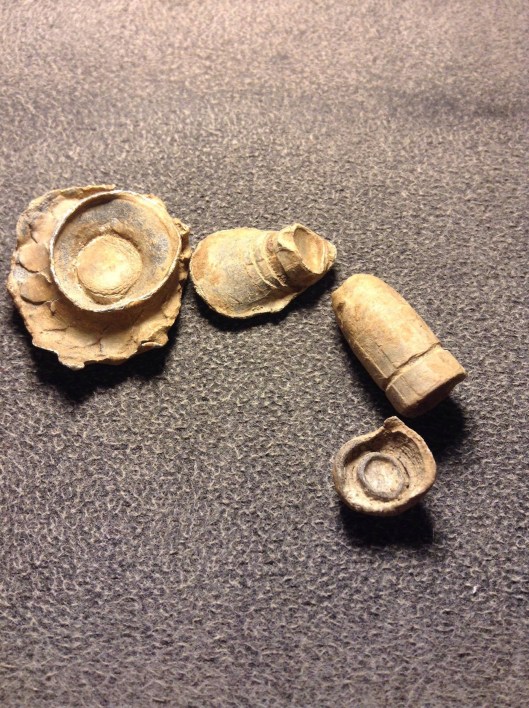
The following newspaper accounts describe the Battle of Kanawha Gap near present-day Chapmanville, Logan County, WV, which occurred on September 25, 1861:
Cleveland (OH) Morning Leader, 3 October 1861
GALLIPOLIS, Oct. 2.
The expedition planned by Col. J.V. Guthrie of the First Kentucky Regiment, and sent out under Lieut. Col. Enyart and Col. Piatt, has returned. They encountered the enemy at Chapmansville under Col. J. Lucien Davis, of Greenbrier, and utterly routed them. The enemy lost between fifty and sixty killed. Our loss was four killed. The expedition returned to Charleston on the 30th ult.

Col. David S. Enyart, 1st Kentucky Infantry (Union).
Evening Star (Washington, DC), 4 October 1861
A Confederate Camp in Western Virginia Broken Up and Routed
CINCINNATI, Oct. 3 — A body of Federal troops, under Lieut. Col. Enyart, attacked a camp of rebels at Chapmansville, in Logan county, Va., near the Kentucky line, routing them, killing sixty and taking seventy prisoners. The same body of rebels were afterward intercepted in their retreat by Col. Piatt, who killed forty and made a large number prisoners.

Col. Abram S. Piatt (1821-1908), 34th Ohio Infantry Regiment.
New York (NY) Herald, 4 October 1861
FIGHT WITH THE REBELS AT CHAPMANSVILLE
Cincinnati, Oct. 3, 1861.
The Kanawha correspondent of the Commercial of this city says that five companies of the First Kentucky regiment, four companies of the Thirty-fourth Ohio regiment and one company of the Fifty Virginia regiment, under Lieutenant Colonel Enyart, surrounded and attacked the rebels at Chapmansville, and after a short engagement completely routed them, killing sixty and taking seventy prisoners. The rebels in escaping were intercepted by Colonial Piatt, who killed forty and took a large number of prisoners. The country between Charleston and Wyandot river is now freed from secession power. This is the most effective blow given the rebels in this part of the valley.
Daily Green Mountain Freeman (Montpelier, VT), 7 October 1861
Chapmansville, Va., the scene of the most recent engagement, is a small post village in Logan county, Va. Logan county is in the extreme Western portion of Virginia, the Tug Fork of the Big Sandy being the boundary line between it and the State of Kentucky. It is one of the largest, wildest and most sparsely inhabited counties in the State.

Part of the Kanawha Gap Battle Site, Chapmanville, Logan County, WV, 9 June 2018.
National Republican (Washington, DC), 7 October 1861
THE SITUATION.
The two affairs at Chapmansville, reported three or four days since, in which the enemy lost one hundred killed and a proportionate number of wounded, will, it is supposed, restore permanent peace to the Virginia counties western of the Kanawha. Chapmansville is on the turnpike from Charleston to Logan county Court-house, and is about twenty-five miles to the south of Barboursville, the shire town of Cabell county. The secessionists in that part of Western Virginia have been numerous and pertinacious. They have once had possession of Guyandotte on the Ohio river and for a long time they threatened Ceredo (Mr. Thayer’s colony,) which lies on the river between Guyandotte and the Kentucky line. There have been two engagements with them in the rear of Ceredo, one at Barboursville, one at Logan county Court-house, one at Boone county Court-house (which town was burnt by the national troops,) and finally two at Chapmansville. The truth is, that in large portions of numerous, and, but for the early occupation of that region by the National troops, would have controlled it, not because they were the majority, but because one secessionist is, everywhere, a match for three Union men.
The secessionists are reckless, violent, and desperate, while their opponents, if not timid are at any rate remarkably pacific. We doubt, indeed, from all the information we can get, whether throwing out of the account Wheeling and Parkersburg, the terminal on the Ohio river of the Baltimore and Ohio railroad, Western Virginia had more elements of Union strength than the Valley of Virginia. From Harper’s Ferry south for fifty miles, the Union men have been numerous from the first, and it is a matter of deep regret that it did not consist with the plans of military strategy adopted at the headquarters of the army here, to occupy (at least) the northern part of the Valley of Virginia. It is consoling, that a different policy was adopted in retrospect to Western Virginia. That region was promptly taken possession of, cleared of the rebel armies by Gen. McClellan, and has since been victoriously held by Gen. Rosecrans. All attempts of the enemy to affect a re-entrance into Western Virginia are promptly repulsed.

Staunton (VA) Spectator, 8 October 1861
Status at Sewell’s Mountain.
The enemy, under Gen. Rozencrantz, and our forces under Gen. Lee, are both upon Sewell Mountain very near each other. A fight has been daily expected there for some time, but the enemy have been fortifying ever since they have been there, and there will not be a fight unless we attack them in their entrenchments. They are afraid to attack us, and it is probable that our force is too weak to risk an attack on them within their fortification. It may, therefore, be some time before an engagement will take place. We understand that we had sent a force of four regiments to their rear for the purpose of cutting off their supplies—that we succeeded in getting around them, but were compelled to return because we did not have sufficient supplies ourselves. We also learn that Col. Jas. W. Davis of Greenbrier, whilst commanding a force of militia in Logan county, attacked a part of the enemy, and was shot down at the first fire. The militia, after several rounds caught the Yankee fever which made their cowardly legs run off with their brave hearts, and they left their commander in the hands of the enemy, who, we fear, has died from his wound.

New historical sign placed by the WV Division of Culture and History located at the 119 ramp in Chapmanville, WV. 26 April 2017.
Chicago (IL) Daily Tribune, 9 October 1861
A Splendid Achievement of the Ohio Zouaves–“Wood Up” the Battle Cry.
[The following letter is exclusively devoted to the fight which the Piatt Zouaves had with the rebels near Chapmansville, Va. It is distinct from the victorious fight which the command of Lieut. Col. Enyart had with another body of rebels, in the same vicinity. EDS. CINCINNATI COM]
CAMP ENYART, KANAWHA, Oct. 2, 1861. EDS. COM.: The Zouave Thirty-fourth Regimens, Ohio, have had a chance to show their metal. This was on Wednesday, on Kanawha Gap, near Chapmansville, Va. After marching 42 miles, they came upon the enemy, who were behind breastworks, but could not stand our boys’ steady fire, for they retreated in utter consternation, their Col. J.W. Davis, of Greenbrier, Va, (but the traitor is a native of Portsmouth, Ohio,) being mortally wounded. We killed 20, took 3 prisoners, a secesh flag, 20 feet long with FIFTEEN STARS, 4 horses, 1 wagon, 10 rifles (one of which I claim), 12 muskets, and commissary stores (very low.) We lost 3 killed, 9 wounded, one since died. The route of the enemy was complete, although they had a brave, skillful commander, and strong position, with two days’ information of our intentions. They fled the moment their commander fell. The fight lasted about 10 minutes opposite the breastworks, but a running fire was kept up previous to that, by the Bushwhackers and rebel cavalry for two hours. At every turn of the road over the mountains, they would fire upon our advance men, wheel round, and gallop away. This kind of fight was kept up till we came suddenly upon their breastworks, immediately in line of our entire column. It was made on the side of a knoll, between two mountain sides, the road running between the mountain on our left. The wily rebel commander had adroitly cut down the brush on the right, placing a force of 100 men on the mountain top on our right, who raked our column from the front to the center. This was to draw our attention from their breastworks. Our men naturally fired upon the rebels on their right, steadily advancing up the road, until within 20 feet of the enemy’s works, when the rebels suddenly opened fire, from their right, left and center. The order from Col. Piatt and Lieut. Col. Toland, to flank right and left was immediately responded to by the Zouaves with a hurrah, a Zouave yell, and a cry of “wood up” from Little Red; a dash by our boys upon the enemy’s breastworks, above which about 300 rebel heads suddenly appeared, unknown by our men till that moment. They sent a perfect storm of bullets around, over, under, and into our men. A few minutes more and our boys were inside the breastworks, chasing them over the mountains, the enemy running away like cowards as they proved to be. They left 29 dead behind. Their force was 450 infantry and 50 cavalry. Our force was 560.
We buried our three brave dead comrades that night, carried our wounded to the house wherein the rebel Colonel lay, mortally wounded, deserted by all his men but one. Our whole column finally marched into the little town of Chapmansville, formerly headquarters of the enemy, and camped for the night.

34th Ohio Volunteer Infantry Regiment, Piatt’s Zouaves, Captain Photo.
Pomeroy (OH) Weekly Telegraph, 11 October 1861
Brilliant Action in the Kanawha Valley.
CHARLESTON, Va., Sept. 30, ’61. Eds. Cin. Com.–Information having been brought to Col. J.V. Guthrie, commanding this post, that a large force of Rebels were gathered at Logan Co., Lt. Col. Enyart, of the 1st Kentucky, was at once sent to engage them. His force was composed of five companies of the 1st Kentucky, four companies of the 34th Ohio–German Regiment–under command of Col. A.S. Piatt, and one company of the 5th Virginia Regiment, under command of Maj. M.H. Wood.
Col. Enyart, with the Kentucky force, surrounded and attacked the Rebels at Chapmanville, and after a short but decisive engagement, completely routed them, killing 60 and taking 70 prisoners. The Rebels, in escaping, were intercepted by Col. Piatt, who surprised them and killed 40 men, and took a large number of prisoners.
The force of the Rebels is now completely broken up, and the country between this point and Guyandotte River is now freed from Secession power. This is the most effective blow given the Rebels in this part of the Valley.
In great haste. Further particulars by next boat.
Very respectfully,
M. CLEMENS,
Lieut. Col. 5th Va. Reg’t.

34th Ohio Volunteer Infantry Regiment, Piatt’s Zouaves, Soldier.
Evening Star (Washington, DC), 11 October 1861
THE BATTLE OF KANAWHA GAP.
The Western Virginia correspondent of the Cincinnati Gazette gives the following account of the late engagement at Kanawha Gap:
There were about 1,050 troops under the command of Colonels Enyart and Piatt, who left their camp Monday morning, 30th ulto., and took up their line of march for the enemy.
The forces moved together until they reached Peytona, on Cole river, where they separated; Col. Enyart going up Cole river. Col. Enyart did not meet the enemy in force at any place but his men did meet and ford swollen rivers, and marched on short rations, and were anxious to meet with the running enemy of Old Virginia. Col. Enyart did not meet Col. Piatt until they met on the Kanawha, on their return.
Col. Piatt’s command immediately proceeded thence to Boone Court House, and camped that night one mile beyond. The next day, after proceeding some sixteen miles,t hey came up with the advance guard of the enemy, consisting of cavalry, when a brisk fire was exchanged, the cavalry retreating. After the retreat of cavalry the battalion was immediately put in order of battle. The advance guard of fifteen men was led forward by Adj’t Clarke, proceeding along the road. Scouts were sent out on either side of the road to meet and repulse the sharp-shooters of the enemy.
The force proceeded in this order for about two miles, meeting the pickets of the enemy, exchanging shots with them incessantly, and driving them back with increased confusion at each charge.
Being unable to ascertain the position of the rebels, the entire force halted for a few moments, and Col. Piatt rode in advance and took observations with his glass, but could not ascertain their force and position, as it was covered with a thick growth of underbrush. After these observations a command was issued to forward the column. The scouts moved on the rapidity and enthusiasm, the main body moving up the narrow road cautiously and firmly. The fire continued to increase, and shots were rapidly exchanged from the right and left with the enemy, until our advanced guard reached within sixty yards of their main force. The column was some eighty yards from the enemy when they received a perfect volley of fire upon their right, indicating that the rebels were in force in that direction. Company “A,” commanded by Capt. Rathbone, was ordered to deploy as skirmishers to the right, up the side of the mountain, and if possible to flank the enemy on the left. Company “C,” commanded by Capt. Miller, was ordered to the right, up a similar mountain, to flank the enemy on their left. Company “I,” commanded by Capt. Anderson, was ordered directly up the ravine, on the left. In this position he drew the concentrated fire of the rebels upon his company, who made use of the knowledge thus obtained by rapidly charging upon and destroying the enemy’s breastworks. The center moved directly up the road. With this disposition of the forces, Col. Piatt routed them from their confusion. Capt. Anderson was the first to mount their breastworks, his men following him in the face of a terrible fire without flinching or confusion.
As Capt. Anderson sealed the breastwork, Capt. Miller closed upon the left and Capt. Rathbone came in upon the right, his men crying “Zouave!” The main column moving up the road in double quick–until they were brought to a temporary halt by obstructions placed in the road by the enemy.
The rebels, terrified by the strange bravery and almost wild enthusiasm that was exhibited by each advancing column, ran in confusion, leaving their dead, wounded, clothing, guns, horses, &c., making their escape by Capt. Rathbone’s right; his company being too far up the mountain to cut off their retreat. Capt. West, commanding company F, was detailed to scour the mountain on the west, on the left of the road. Capt. O.P. Evans on the west side of the mountain, on the right side of the road. Capt. Herman Evans, commanding Company H, on the east side of the mountain, on the left of the road.
Each of these companies moved with dispatch, yet such was the knowledge of the rebels of teh by-paths in the mountains, and belonging to the “F.F.V.’s,” and having been drilled at running all summer, that but two were captured.
Among interesting objects captured was a genuine secession flag, captured by Lieut. Brown.
The enemy’s loss was thirty killed and fifty wounded.
We regret to know that four of our men were killed and eight wounded.

34th Ohio Volunteer Infantry Regiment, Piatt’s Zouaves, Soldiers. Here’s a link to Captain T.W. Rathbone’s Civil War diary: http://resources.ohiohistory.org/ohj/browse/displaypages.php?display[]=0071&display[]=33&display[]=56
, 12 October 1861
The fight at Chapmansville was a sharp and bloody affair. Five of Piatt’s Zouaves were killed. The rebels lost thirty-five killed.

Part of the Kanawha Gap Battle Site, Chapmanville, Logan County, WV, 9 June 2018.
National Republican (Washington, DC), 17 October 1861
The thirty-fourth regiment (first Zouaves) have been actively engaged since they came to the Kanawha Valley. Since the glorious victory they won near Chapmansville where the rebel commander, Colonel Davis, was mortally wounded, the Union sentiment has advanced on the Cole River. Two companies have been organized, and are ready to go to work to defend their own homes and give the organized regiments an opportunity to advance into the heart of the enemy’s country.

Part of the Kanawha Gap Battle Site, Chapmanville, Logan County, WV, 9 June 2018.
Cincinnati (OH) Daily Press, 22 October 1861
Captain H.C. Evans, of Piatt’s Zouave Regiment, yesterday called in our office and exhibited a Secesh flag, captured at the Chapmansville fight, on the 24th ult.

34th Ohio Volunteer Infantry Regiment, Piatt’s Zouaves, Soldiers.
Clarksville (TN) Chronicle, 25 October 1861
The Fight in Logan County, Va.
[From the Richmond Whig of the 15th.]
We yesterday published the Yankee account of a battle in Logan county, which as usual, was manufactured out of whole cloth. The following are the facts as given by the South-western Times, (Tazewell county) of the 10th inst.:
From Samuel Smoot, Esq., of Boone county, who was in the fight, we learn the following particulars of the battle near Chapmanville, Logan county, on the 25th ult: The Yankees numbered 700, and commenced the attack upon our troops–the Logan militia–in a low gap between Guyandotte river and Big Creek, where they were engaged in raising a temporary breastwork. Our troops numbered 220, but there were only about 80 of them engaged in the fight. They were commanded by Col. J.W. Davis, of Greenbrier, a brave and gallant officer, who was severely, but not dangerously wounded, in the arm and breast. As soon as it became known that Col. Davis was wounded, the militia commenced a retreat. The commanding officer of the Lincoln troops afterwards confessed to Col. Davis, who was taken prisoner, that at the same moment a portion of the Yankees were running, and that one more round would have completely dispersed them.
The loss of the Yankees, by their own confession to Col. Davis, was 40 killed and a number wounded; among the former were four Union men, all of whom are represented by the Yankees to be most arrant thieves and cowards. Our loss was two killed and three or four wounded, besides Col. Davis, whose valuable services are at present lost to the Confederacy, being paroled by the enemy.
On the following day our scouts killed one of their pickets, and wounded another, at a point about half way between Logan Court House and Chapmanville, promising to give them particular thunder before daylight next morning. This with some news from a lady on the road, and some account of the militia of the surrounding counties, found on the person of Col. Davis, caused a hasty stampede for their headquarters, in the valley of the Kanawha. It seems that high water, bad roads, nor anything else could impede their rapid flight. They tore down a meeting house in Boone county to make rafts whereon to cross the river. They drowned two of their wounded, lost a wagon containing their entire stock of ammunition, and were fully persuaded that they were followed by two thousand cavalry, of which the Yankees in the West are about as fearful as their Eastern brothers are of masked batteries.
Upon the whole, we are much gratified at the result of this fight. It has, for the present, driven the cowardly thieves from the country, given renewed energy to the true patriots of Logan and the adjoining counties, fully convincing them that with the assistance of two or three hundred of their gallant friends in Tazewell county, they will be fully able to thrash any number that Gen. Cox or his friends shall dare to send against them.”
Note: An almost identical version of this story appeared in the Staunton (VA) Spectator on 22 October 1861.

Record relating to the 129th Virginia Militia (Confederate), which was present at the Battle of Kanawha Gap.